What happens when you type a URL in the web browser?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
06 Feb 2020

Ever wondered what happens when you type a URL in the browser? It is a commonly asked question in technical interviews. In this blog, we will see what happens in the background, step by step when we type any URL. So, let's get started.
1. You enter the URL in the browser.
Suppose you want to visit the website of AfterAcademy. So you type afteracademy.com in the address bar of your browser. When you type any URL you basically want to reach the server where the website is hosted.
2. The browser looks for the IP address of the domain name in the DNS(Domain Name Server).
DNS is a list of URLs and their corresponding IP address just like the telephone book has phone numbers corresponding to the names of the people. We can access the website directly by typing the IP address but imagine remembering a group of numbers to visit any website. So, we only remember the name of the website and the mapping of the name with the IP address is done by the DNS.
The DNS checks at the following places for the IP address.
- Check Browser Cache: The browser maintains a cache of the DNS records for some fixed amount of time. It is the first place to run a DNS query.
- Check OS Cache: If the browser doesn't contain the cache then it requests to the underlying Operating System as the OS also maintains a cache of the DNS records.
- Router Cache: If your computer doesn't have the cache, then it searches the routers as routers also have the cache of the DNS records.
- ISP(Internet Service Provider) Cache: If the IP address is not found at the above three places then it is searched at the cache that ISP maintains of the DNS records. If not found here also, then ISP’s DNS recursive search is done. In "DNS recursive search", a DNS server initiates a DNS query that communicates with several other DNS servers to find the IP address.
So, the domain name which you entered got converted into a DNS number. Suppose the above-entered domain name afteracademy.com has an IP address 100.95.224.1. So, if we type https://100.95.224.1 in the browser we can reach the website.
3. The Browser initiates a TCP connection with the server.
When the browser receives the IP address, it will build a connection between the browser and the server using the internet protocol. The most common protocol used is TCP protocol. The connection is established using a three-way handshake. It is a three-step process.
- Step 1 (SYN): As the client wants to establish a connection so it sends an SYN(Synchronize Sequence Number) to the server which informs the server that the client wants to start a communication.
- Step 2 (SYN + ACK): If the server is ready to accept connections and has open ports then it acknowledges the packet sent by the server with the SYN-ACK packet.
- Step 3 (ACK): In the last step, the client acknowledges the response of the server by sending an ACK packet. Hence, a reliable connection is established and data transmission can start now.
4. The browser sends an HTTP request to the server.
The browser sends a GET request to the server asking for afteracademy.com webpage. It will also send the cookies that the browser has for this domain. Cookies are designed for websites to remember stateful information (items in the shopping cart or wishlist for a website like Amazon) or to record the user’s browsing history etc. It also has additional information like request header fields(User-Agent) for that allows the client to pass information about the request, and about the client itself, to the server. Other header fields like the Accept-Language header tells the server which language the client is able to understand. All these header fields are added together to form an HTTP request.
Sample Example of HTTP Request: Now let’s put it all together to form an HTTP request. The HTTP request below will fetch abc.html page from the web server running on afteracademy.com
GET /abc.htm HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE5.01; Windows NT)
Host: www.afteracademy.com
Accept-Language: en-us
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: Keep-Alive
5. The server handles the incoming request and sends an HTTP response.
The server handles the HTTP request and sends a response. The first line is called the status line. A Status-Line consists of the protocol version(e.g HTTP/1.1) followed by numeric status code(e.g 200)and its associated textual phrase(e.g OK). The status code is important as it contains the status of the response.
- 1xx: Informational: It means the request was received and the process is continuing.
- 2xx: Success: It means the action was successful.
- 3xx: Redirection: It means further action must be taken in order to complete the request. It may redirect the client to some other URL.
- 4xx: Client Error: It means some sort of error in the client’s part.
- 5xx: Server Error: It means there is some error on the server-side.
It also contains response header fields like Server, Location, etc. These header fields give information about the server. A Content-Length header is a number denoting the exact byte length of the HTTP body. All these headers along with some additional information are added to form an HTTP response.
Sample Example of HTTP Response: Now let’s put it all together to form an HTTP response for a request to fetch the abc.htm page from the web server running on afteracademy.com.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Tue, 28 Jan 2020 12:28:53 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.14 (Win32)
Last-Modified: Wed, 22 Jul 2019 19:15:56 GMT
Content-Length: 88
Content-Type: text/html
Connection: Closed
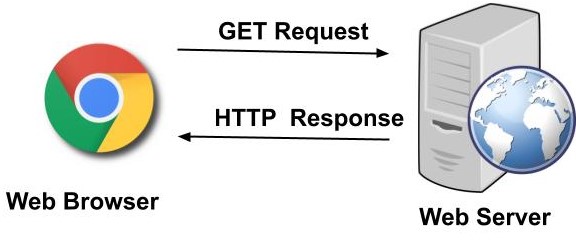
6. The browser displays the HTML content.
Now the browser gets the response and the HTML web page is rendered in phases. First, it gets the HTML structure and then it sends multiple GET requests to get the embedded links, images, CSS, javascript files, etc and other stuff. The web page will be rendered and in this case, the afteracademy web page will be displayed.
All these steps happen each time we enter any URL. All these processes happen in the background and within milliseconds. That's it for this blog. Hope you enjoyed reading this blog.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the different types of relationships in DBMS?
In this blog, we will study various types of relationships in DBMS which help in defining the association between various entities. Also, we will discuss the types of participation constraints which may exist between the relationship and the entity type.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is semaphore and what are its types?
In this blog, we will learn about semaphores and we will also see the types of semaphore. We will see how semaphores can be used to achieve process synchronization.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is Fragmentation and what are its types?
In this blog, we will learn about the fragmentation problem that occurs during memory allocation. We will also study the types of fragmentation i.e. internal fragmentation and external fragmentation.
AfterAcademy Tech
MVC Architecture in Web Applications
MVC architecture has become an extremely common and favoured design pattern for creating web applications. Let us explore more and learn why is it so famous and preferred in the world of web design.
