Topological Sorting
AfterAcademy Tech
•
01 May 2020
In this blog, we will discuss Topological sort in a Directed Acyclic Graph i.e. DAG. We will discuss the following things:
- What is the Topological Sort?
- How can we find Topological Ordering?
- Illustration using a Directed Acyclic Graph
- Pseudo Code
- Applications of Topological Sorting
Prerequisites
- Introduction to Graph in Programming
- Graph Traversal: Depth First Search
- Graph Traversal: Breadth-First Search
What is Topological Sort
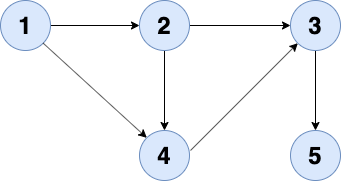
In the Directed Acyclic Graph, Topological sort is a way of the linear ordering of vertices v1, v2, …. vN in such a way that for every directed edge x → y, x will come before y in the ordering.
For example-The topological sort for the below graph is 1, 2, 4, 3, 5
Important Points to remember
- There can be multiple topological ordering for a Directed Acyclic Graph.
- In order to have a topological sorting, the graph must not contain any cycles and it must be directed i.e. the graph must be a DAG. (Think!)
How to find Topological Sort
Topological order can be one of the subsets of all the permutations of all the vertices following the condition that for every directed edge x → y, x will come before y in the ordering.
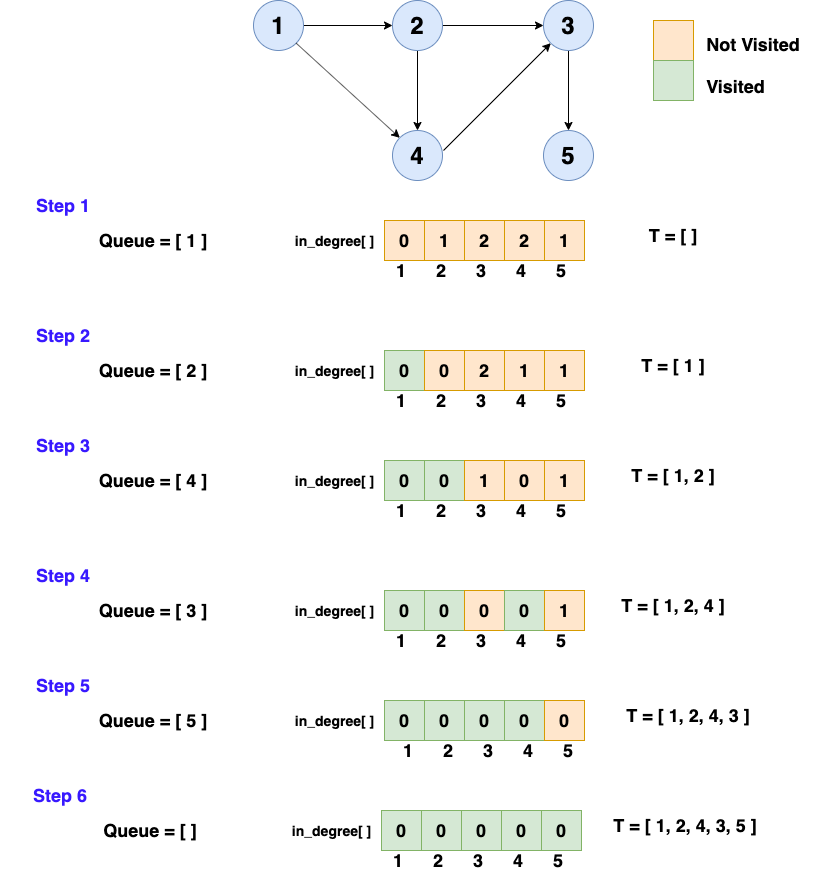
For that, we will maintain an array T[ ], which will store the ordering of the vertices in topological order. We will store the number of edges that are coming into a vertex in an array in_degree[N], where the i-th element will store the number of edges coming into the vertex i. We will also store whether a certain vertex has been visited or not in visited[N]. We will follow the belo steps:
- First, take out the vertex whose
in_degreeis 0. That means there is no edge that is coming into that vertex. - We will append the vertices in the Queue and mark these vertices as visited.
- Now we will traverse through the queue and in each step we will
dequeue()the front element in the Queue and push it into the T. - Now, we will put out all the edges that are originated from the front vertex which means we will decrease the
in_degreeof the vertices which has an edge with the front vertex. - Similarly, for those vertices whose
in_degreeis 0, we will push it in Queue and also mark that vertex as visited. (Hope you must be thinking its BFS but with in_degree)
Illustration
Pseudo Code
topological_ordering(int N, bool adj[N][N])
{
int T[]
bool visited[N]
int in_degree[N]
for ( i = 0 to N-1 )
in_degree[i] = visited[i] = false
for ( i = 0 to N-1 )
for ( j = 0 to N-1 )
if (adj[i][j] == true)
in_degree[j] += 1
Q = Queue()
for ( i = 0 to N-1 )
{
if ( in_degree[i] == 0 ) {
Q.enqueue(i);
visited[i] = true
}
}
while( Q.size() != 0 )
{
curr = Q.front()
Q.dequeue();
T.append(curr);
for( j = 0 to N-1 )
{
if ( adj[curr][j] == true and visited[j] == false)
{
in_degree[j] -= 1
if (in_degree[j] == 0)
{
Q.enqueue(j)
visited[j] = true
}
}
}
}
return T
}
Applications
- Scheduling jobs from given dependencies among Jobs. For example, if some job requires the dependency of some other job, then we can use topological sorting.
- Instruction Scheduling
- Determining the order of compilation tasks to perform in makefiles, data serializations and resolving symbol dependencies in linkers.
- Use in maven dependency resolutions.
Critical Ideas to Think
- The above approach uses the BFS traversal technique. Can it be solved using the DFS traversal technique?
- What can be the modifications that can be done if we have been given the Adjacency matrix?
Graph questions
- Is Graph Bipartite?
- Number of Islands
- Word Ladder Problem
- Smallest Multiple with 0 and 1
- Course Schedule
- Knight on Chessboard
Happy Learning, Enjoy Algorithms!
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Sort List - Merge Sort
Sort a linked list using Merge Sort. This is a very famous interview problem that demonstrates the concept of recursion. This problem is quite similar to Merge Sort in Arrays.

AfterAcademy Tech
Introduction To Sorting Algorithms - Selection and Insertion sort
Sorting is a famous problem solving approach during the interview. In this blog, we are going to discuss about the insertion and selection sort algorithm.

AfterAcademy Tech
Sort a linked list using Insertion Sort - Interview Problem
Sort a linked list using insertion sort and return its head.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is network topology and types of network topology?
In this blog, we will learn about various network topologies, their advantages and disadvantages in a computer network.
