Distribute Candy Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
08 Aug 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
There are N children standing in a line with some rating value. You want to distribute a minimum number of candies to these children such that:
- Each child must have at least one candy.
- The children with higher ratings will have more candies than their neighbours.
You need to write a program to calculate the minimum candies you must give.
- Input: An array
arr[]of N integers representing the ratings of each student
Example 1
Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 2]
Output: 4
Explanation: You can distribute to the first, second and third child 1, 2 and 1 candies respectively. The third child gets 1 candy because it satisfies the above two conditions.
Example 2
Input: arr[] = [1, 5, 2, 1]
Output: 7
Explanation: Candies given = [1, 3, 2, 1]
Solution
We will be discussing two different solutions to this problem:-
- Brute Force: One by one distribute candies to each child until the condition satisfies.
- Greedy using an array: Traverse the array twice, from left to right and right to left while greedily determining the minimum number of candies required by each child.
You may try this problem here.
1. Brute Force Approach
The most straight forward approach for this problem would be to start with distributing one candy to each child and then check if any child who has more rating than his one of the neighbours should have more candy than its neighbour. So, distribute one more candy to that child who does not satisfy the above condition. Do this until every child is satisfied.
Solution Steps
Create a 1-D candy array that will represent the number of candies given to each child corresponding to the rating array. The question states that each child must have at least one candy so, initialize each index of candy array by one.
- Now, iterate over the rating array and check if the
ithchild rating is higher than(i-1)thchild, thencandy[i]should be greater thancandy[i-1]. So, updatecandy[i] = candy[i-1]+1. - Similarily, if the
ithchild rating is greater than(i+1)thchild, thencandy[i]should be greater thancandy[i+1]. So, updatecandy[i] = candy[i+1] + 1.
Do the above two steps until no update in the number of candies required for any child.
Ultimately return the sum of candy array which will be the minimum number of candies required.
Pseudo Code
int candy(int[] ratings, int size) {
int[size] candies = {1}
bool flag = true
while (flag) {
flag = false
for (int i = 0 to i < size) {
if (i != size - 1 and ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1] and candies[i] <= candies[i + 1]) {
candies[i] = candies[i + 1] + 1
flag = true
}
if (i > 0 and ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1] and candies[i] <= candies[i - 1]) {
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1
flag = true
}
}
}
int sum = 0
for (int i = 0 to i < size) {
sum += candies[i]
}
return sum
}
Complexity Analysis
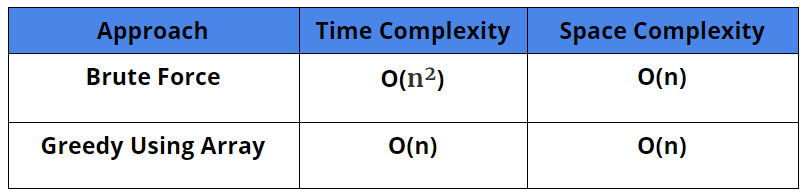
Time Complexity: O(n²)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical ideas to Think!
- Why are we increasing the number of candies only by one whenever
rating[i] > rating [i-1]? - What are the edge cases for this problem and how did we handle it above?
- Explain how time complexity is O(n²)?
2. Greedy, Using Array
Let’s divide the problem condition “children with higher ratings will have more candies than their neighbours” into two parts.
- Find the minimum number of candies given to the
child[i]who have a higher rating thanchild[i-1] - Find the minimum number of candies given to the
child[i]who have a higher rating thanchild[i+1]
For the above two problems, we can maintain two 1D arrays that will save the number of candies given to each child in each case.
- For the first problem, we can move from left to right while checking rating[i] > rating[i-1], if so then child[i] will have candy[i-1] +1, else child[i] will have one candy.
- For the second problem, we can move from right to left while checking rating[i] > rating[i+1], if so then child[i] will have candy[i+1] +1, else child[i] will have one candy.
Now, just taking the max value of each index of the two arrays will represent the minimum number of candies required by each child corresponding to the index.
Solution Steps
- Create two 1D arrays, say
left2rightandright2left,and initialize each index by 1.(Why?) - In the first pass, check if
rating[i] > rating[i-1]then updateleft2right[i]with the previous value + 1 - In the second pass in reverse order, check if
rating[i] > rating[i+1]then updateright2left[i]with the previous value + 1 - The minimum number of candies each child would get will be the max of
left2right[i]andright2left[i]
Pseudo Code
int candy(int[] ratings, int size) {
int sum = 0
int[size] left2right = {1}
int[size] right2left = {1}
for (int i = 1 to i < size) {
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) {
left2right[i] = left2right[i - 1] + 1
}
}
for (int i = size - 2 to i >= 0) {
if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) {
right2left[i] = right2left[i + 1] + 1
}
}
for (int i = 0 to i < size) {
sum += max(left2right[i], right2left[i])
}
return sum
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical ideas to Think!
- Try some sample test cases and run this algorithm to get a clear understanding of what’s happening behind the hood.
- Why did we return the sum of
max(left2right[i], right2left[i])for eachi? - Can you solve this problem with only one auxiliary array instead of two arrays?
Answer: Yes, you will notice that after the second pass in the above approach, we are only maintaining the max of each index from the two arrays. We can simply remove the second array and can update the first array like this,
left2right[i] = max(left2right[i], left2right[i + 1] + 1)
whenever rating[i] > rating[i+1]
and at last, return the sum of left2right.
Comparison Of Different Solutions
Suggested Problem To Solve
- Chocolate Distribution Problem
- Huffman Coding
- Minimum product subset of an array
- Maximize the sum of arr[i]*i
- Largest lexicographic array with at-most K consecutive swaps
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding!
Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Fractional Knapsack Problem
This is an interview problem asked by companies like Amazon. This problem is based on Greedy Algorithm and is one of the very basic problem for understanding Greedy Algorithms.

AfterAcademy Tech
Min Stack Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Yahoo and Adobe. The problem is to design a stack that will support push(), pop(), top() and getMin() operation in constant time. We will be discussing two different ways to approach this problem.

AfterAcademy Tech
The Reader-Writer Problem in Operating System
In this blog, we will learn about the classic reader-writer problem in Operating System. We will also see how to remove this problem in Operating System.

AfterAcademy Tech
The Producer-Consumer problem in Operating System
In this blog, we will learn about the Producer-Consumer problem in Operating System and we will also learn how to solve this problem. It is used in multi-process synchronization.
