Calculate power function
AfterAcademy Tech
•
07 Feb 2020
Understanding the Problem
Given two integers x and n, write a function to compute x^n (x to the power n). You may consider that x and n are small and overflow doesn’t happen.
Example —
power(3,4) = 81
power(2,-3) = 0.125
Solutions
- Naive Iterative approach
- Divide and Conquer approach
- Optimized divide and conquer approach
1. Naive Iterative approach
The most basic way to calculate the nth power of a number is to multiply that number exactly n-times.
What if n is negative, like pow(2,-3) = 0.125
In this case, we could just find the inverse of its positive power i.e. pow(2,-3) = 1/(2^3).
Solution steps
- Declare and initialize a variable to store power say
power = 1. - Run a loop from 1 to exponent, increment loop counter by 1 in each iteration.
- For each iteration inside loop multiply power with the number.
- For negative exponent, return
1/powerOtherwise, returnpower
Pseudo Code
float power(int base, int expo){
bool isNegative = False
if(expo < 0){
isNegative = True
}
float power = 1
for(int i = 1 to abs(expo)){
power = power * base
}
if(isNegative) {
return (1/power)
}
return power
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity — O(n) or O(exponent)
Space Complexity — O(1)
Critical Ideas to Think
- Will the algorithm work if the input base is negative?
- Will the algorithm work if the input exponent is negative?
- Are you able to think of a better approach to solve it?
2. Divide and Conquer approach
The Divide & Conquer approach squares the number each time, rather than multiplying it with the number itself.
Now if we try to visualize this process recursively, then it would be like this →
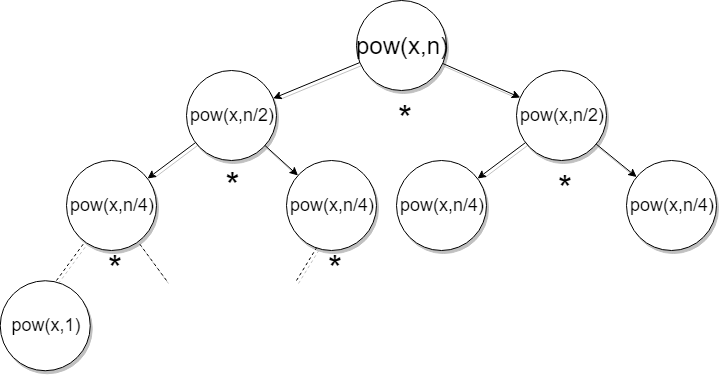
Example — If we want to compute 3⁸ we actually compute it like
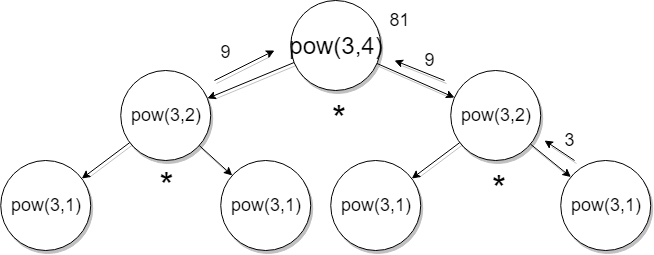
So the recursive definition would be →
if exponent is even :
power(base, expo) = power(base, expo/2) * power(base, expo/2)
if exponent is odd :
power(base, expo) = base * power(base, expo/2)*power(base, expo/2)
Solution steps
- Check if the exponent is 0 then return 1 otherwise
- On the basis of even or odd, call the power function recursively as defined above.
Pseudo Code
float power(int base, int expo) {
if (expo is 0)
return 1
if (expo % 2 == 0)
return power(base, expo / 2) * power(base, expo / 2)
else {
if(expo > 0)
return (power(base, expo / 2) * power(base, expo / 2))* base
else
return (power(base, expo / 2) * power(base, expo / 2))/ base
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity — O(n) or O(exponent)(Why?)
Space Complexity — O(log(n)) (Think!)
Critical Ideas to Think
- Can you point out repeating calculations?
- Will this algorithm work for a negative exponent value?
3. Optimized divide and conquer approach
If you will look over the previous divide and conquer approach recursive diagram, you will find out that at each step we are recalculating the power of the base at each level i.e. same power is counted twice.
So, instead of calling the power function twice recursively, we could just square the power function once. In this way, we could optimize the time complexity.
Pseudo Code
float power(int base, int expo) {
if (expo is 0)
return 1
temp = power(base, expo/2)
if (expo % 2 == 0)
return temp * temp
else{
if(expo > 0)
return temp * temp * base
else
return temp * temp / base
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(log n) or O(log expo)
Space Complexity: O(log n) or O(log expo) due to recursive stack space
Critical Ideas to Think
- Can you think of a better approach than this?
- Dry run this algorithm on a few examples.
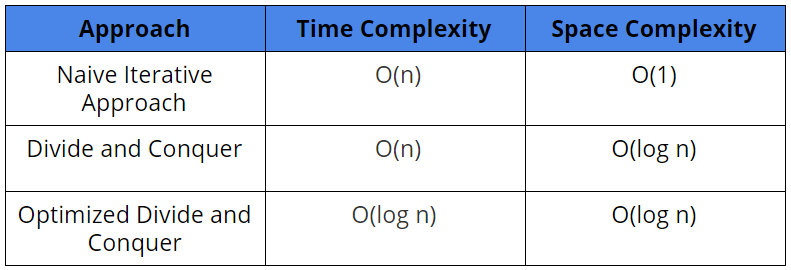
Comparison of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Calculate the square root of a number
- Calculate the value of nCr
That's it for this blog. Hope you learned something new today.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are aggregate functions?
In this blog, we will learn about some of the aggregate functions that are used in SQL. These aggregate functions take more than one value and return one value as a result.

AfterAcademy Tech
Mastering Activation Functions in Neural Networks
In this blog, we are going to learn what is activation function and it's types. We will also learn what is a good Activation function and when to use which Activation function in Neural Network.

AfterAcademy Tech
What are Scalar functions?
In this blog, we will learn about some of the Scalar functions that are used in SQL.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is an Operating System and what are the goals and functions of an Operating System?
In this blog, we will learn what an Operating System is and what are the goals of an Operating System. We will also learn the functionalities of an Operating System that helps in achieving the goal of the OS.
