Spiral Order Traversal of a Matrix
AfterAcademy Tech
•
19 Dec 2019

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given a 2-dimensional array or a matrix, we have to traverse the given matrix in spiral order. For better understanding of what a spiral order traversal looks like, have a look at the below given diagram: →
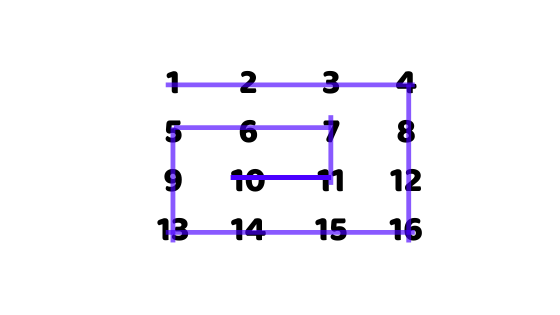
Input: A[][4]=
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
Output: 1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
Similarly, let's consider another example
Input: A[][4]=
8 9 11 14
16 21 20 24
31 13 40 42
52 70 30 34
Output: 8 9 11 14 24 42 34 30 70 52 31 16 21 20 40 13
Possible follow-up questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Can I to modify the given matrix?(Ans: No)
Solution by Iterative Approach
How would we do the spiral order traversal of the given matrix with a pen? We will start from the first row and first column and will continue drawing a spiral through the matrix.
Solution idea:
We will do the same traversal as discussed starting from the first row and column in all the four directions: →
- Left to Right
- Top to Bottom
- Right to Left and
- Bottom to Top
Solution steps
- We will use four loops to traverse in the four directions. Each loop for a single direction.
- Also, we will use four variables to indicate the start of the row index, end of the row index, the start of the column index and end of the column index.
Pseudo-Code
void spiralOrderTraversal(int end_row, int end_col, int A[R][C])
{
int i
int start_row = 0
int start_col = 0
while(start_row < end_row && start_col < end_col)
{
for(i = start_col to end_col-1; i=i+1)
{
print(A[start_row][i])
}
start_row = start_row + 1
for(i = start_row to end_row-1; i=i+1)
{
print(A[i][end_col - 1])
}
end_col = end_col - 1
if(start_row < end_row)
{
for(i = end_col-1 to start_col; i=i-1)
print(A[end_row-1][i])
end_row = end_row - 1
}
if(start_col < end_col)
{
for(i = end_row-1 to start_row; i=i-1)
print(A[i][start_col]
start_col = start_col + 1
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis:
We are traversing and printing each element of the matrix once.
Time Complexity: O(R*C)(Here R refers to the number of rows and C refers to the number of columns in a matrix)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Solution by Recursive approach
We can solve the above problem with recursion following the similar approach by just printing the boundary of the matrix. In every recursive call, the size of the matrix is decreased and again the boundary of the newly small matrix with decreased dimension is printed.
Pseudo-Code
void spiralOrderTraversal(int A[R][C], int start_row, int start_col, int end_row, int end_col)
{
if(start_row >= end_row || start_col >= end_col)
return
for(int i = start_row to end_col; i=i+1)
print A[start_row][i]
for(int i = start_row+1 to end_row; i=i+1)
print A[i][end_col-1]
if((end_row-1) != start_row)
{
for(int i = end_col-2 to start_col; i=i-1)
print(A[end_row-1][i]
}
if((end_col-1) != start_col)
{
for(int i = end_row-2 to start_row; i=i-1)
print(A[i][start_col]
}
spiralOrderTraversal(A, start_row+1, start_col+1, end_row-1, end_col-1)
}
Critical ideas to think!
- Can you think of the time and space complexity of the recursive solution?(Hint: It is based on the same approach of traversing and printing each element.)
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Form a spiral matrix from a given array
- Print a matrix in reverse wave form
- Level Order Traversal in spiral form
- Print a matrix in a spiral form starting from a point
- Print a matrix in a reverse spiral form
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithm!!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Tree Zig Zag Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e, from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between). The problem is a typical Interview problem based on Tree Traversal

AfterAcademy Tech
How to traverse in a tree?
It is important to know traversal techniques in a tree before solving tree problems. We have discussed the 3 primary traversals in a tree at length in this blog with both recursive and iterative implementations.

AfterAcademy Tech
Rotate Matrix
Given a square matrix, turn it by 90 degrees in the clockwise direction.

AfterAcademy Tech
Graph Traversal: Depth First Search
In this blog, we will learn Depth First Search that is used for Graph Traversal i.e. the Depth First Search is used to traverse each and every node of a graph. So, let's learn together.