Search an element in a sorted and infinite array
AfterAcademy Tech
•
17 Oct 2019

Difficulty Level: Hard
Asked in: Amazon
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: You are given a sorted and infinite array A[] and an element K. You need to search for the element K in the array. If found, return the index of the element, else return -1.
For Example :
Input: A[] = {1,3,5,8,12,13,17,19,28,39,103,123,140,2040,…}, K = 17
Output: 6
Input: A[] = {10,20,25,30,67,93,159,192,350,1230,1341,4533,…}, K = 23
Output: -1
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- What is the meaning of infinite array ? (Ans: We don't know the upper bound of the array)
- How big can the resultant index be? (Ans: Ignore the integer overflow problem, we just want to check your logic, let us assume integer overflow won’t occur)
Brute force and Efficient solutions
We will be discussing three solutions for this problem:-
- Brute Force approach : Using linear Search
- Increment by a constant value and using binary search
- Increment by an exponential order and using binary search
1. Brute Force approach : Using linear Search
In the infinite array, we don’t know the upper bound to apply the binary search. So simple solution we could think to start searching for K linearly from index 0 until you you find an element equal to K, then return the index. If you find an element greater than K, then return -1.
Pseudo-Code
int search_infiniteArray(int A[], int K)
{
int i = 0
while (A[i] <= K)
{
if(A[i] == K)
return i
else
i = i + 1
}
return -1
}
Complexity Analysis
Let i be the position of the element to be searched, then the time Complexity = O(i) (Think)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Since we know that the array is sorted, Can we use this info to improve the time complexity?
2. Increment by a constant value and using binary search
If we can track the interval (with the lower and upper bound) where target value reside then we can apply the binary search in that interval. Here we maintain the interval size by constant value C.
Note: In a sorted array, if we check an element at any index j, we could logically know the relative position of element K with respect to A[j].
Solution Steps
- Initialize lower and upper index of the interval i.e. l = 0 , r = C
- Compare the K with the value present at the upper index of the interval
- if K > A[r] then copy the upper index in the lower index and increase the upper index by C. Keep on doing this until you reach a value that is greater than K.
- If K < A[r], apply binary search in the interval from l to r
3. If found, return the index else return -1.
Pseudo-Code
int search_infiniteArray( int A[], int K )
{
int l = 0
int r = C
while (A[r] < K)
{
l = r
r = r + C
}
return binarySearch(A, l, r, K)
}
Complexity Analysis
Let i be the position of the element to be searched, then the number of iterations for finding upper index 'r' is equal to i/C in the worst case (Think).
Hence time complexity = Finding the upper index 'r' of the interval + Binary Search in the interval from l to r = O(i/C) + O(logC) = O(i)
Space Complexity = O(1) if we use an iterative binary search.
Critical ideas to think
- How should we optimally choose the value of C ? What will happen when we choose a very large arbitrary value?
- How can we improve the search time-complexity significantly?
3. Increment by an exponential order and using binary search
In this approach, we increase the interval size by an exponential order of 2. We call this approach exponential search which helps us to track the upper bound quickly in comparison to the previous approach.
Pseudo-Code
int search_infiniteArray( int A[], int K )
{
int l = 0
int r = 1
while (A[r] < K)
{
l = r
r = 2*r
}
return binarySearch(A, l, r, K)
}
Complexity Analysis
Let i be the position of the element to be searched, then the number of iterations for finding upper index 'r' is equal to O(log i) in the worst case. Similarly, The total number of elements between l and r = O(i) (Think)
Time complexity = finding uppar index 'r' of the interval + Binary Search from l to r = O(log i) + O(log i ) = O(log i)
Space Complexity: O(1) if we use iterative binary search.
Critical ideas to think!
- What would be the value of l and r after m iteration of the loop? How the worst-case time complexity for binary search is O(log i)?
- Would multiplying indices by a higher order than 2 help us to improve the time complexity?
- Can we apply the exponential search in the case of bounded arrays? If yes then, in which situation it can perform better than binary search?
- What would be the space complexity if we use a recursive binary search?
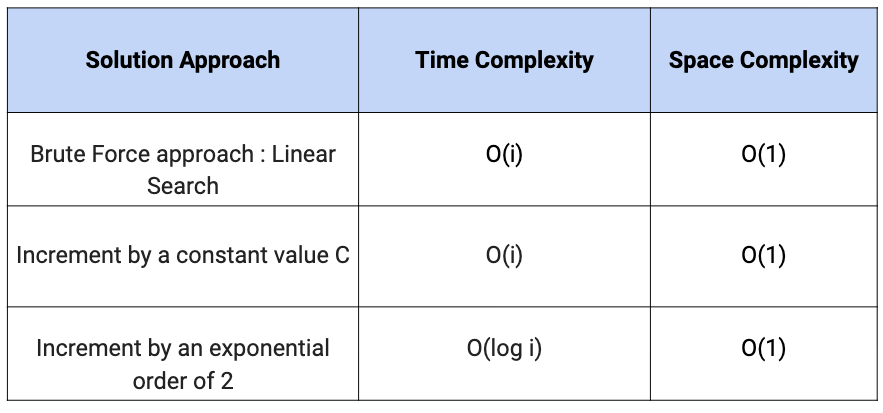
Comparison of different solutions
Let i be the position of the element to be searched.
Suggested Problems to solve
- Find the index of first 1 in an infinite sorted array of 0s and 1s
- Find the point where a monotonically increasing function becomes positive first time
- Search an element in a sorted and rotated array
- Find the maximum element in an array which is first increasing and then decreasing
- Find the first and last occurrence of a number in a sorted array
Please write comments if you find any error or bug. Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Search For A Range In Sorted Array
Given a sorted array A[] with possibly duplicate elements, write a program to find indexes of first and last occurrences of an element k in the given array. This question will clear your concept of Binary Search

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum in a Sorted and Rotated array
You have a sorted and rotated array where elements are sorted and rotated circularly. Write a program to find the minimum element in the array.
AfterAcademy Tech
Largest Element In An Array
Given an array arr[] of size n , write a program to find the largest element in it. To find the largest element we can just traverse the array in one pass and find the largest element by maintaining a max variable.