Divide and Conquer Approach in Programming
AfterAcademy Tech
•
16 Dec 2019

Divide and Conquer Introduction
Divide and Conquer is a recursive problem-solving approach which break a problem into smaller subproblems, recursively solve the subproblems, and finally combines the solutions to the subproblems to solve the original problem. This method usually allows us to reduce the time complexity to a large extent.
We will be discussing the Divide and Conquer approach in detail in this blog. We will be exploring the following things:
- Phases of Divide and Conquer approach
- Example 1: Binary Search
- Example 2: Merge Sort
- Problem solving concepts/tips
- Critical concepts to explore further
- Important Problems/Real-Life Applications
- Suggested Problems to solve
Phases of Divide and Conquer
It consists of three phases:
- Divide: Dividing the problem into two or more than two sub-problems that are similar to the original problem but smaller in size.
- Conquer: Solve the sub-problems recursively.
- Combine: Combine these solutions to subproblems to create a solution to the original problem.
Example 1: Binary Search
Problem Statement: Given a sorted array A[] of size n, you need to find if element K is present or not. If yes then return true otherwise return false.
Solution Idea: The naive solution for the problem do a linear search to check whether element K is present or not. This will take O(n) time complexity. But if we use the sorted property of the array, we can apply the divide and conquer approach to solve it efficiently in O(log n) time complexity.
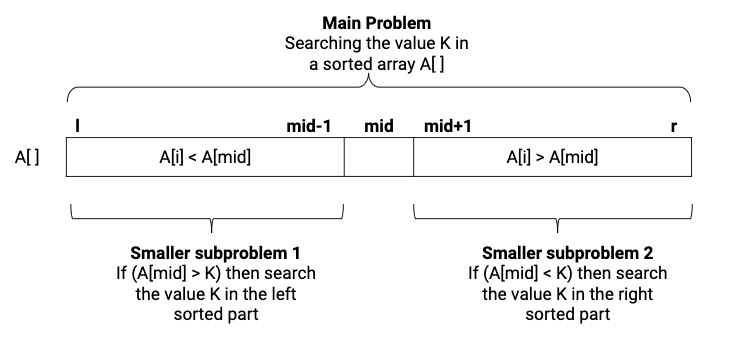
The basic idea of binary search is to divide the array equally and compare the value K with the middle element. If A[mid] is greater than K then definitely K will not be present in the right part, so we search value K in the left part. Similarly, if A[mid] is less than K then we search value K in the right part. (Think!)
Solution Steps
Recursive Call : binarySearch(A[], l, r, k)
- Divide: Calculate the middle index of the array. if(A[mid] == k),then return 1. This is a case of a successful search.
- Conquer: Recursively solve the smaller sub-problem
- if (A[mid] > k), then call binarySearch(A, l, mid-1, k)
- if (A[mid] < k), then call binarySearch(A, mid+1, r, k)
- Combine: Combine part is trivial here(Think!)
- Base Case: if (l > r) then return -1. This is the case of an unsuccessful search (Think!)
Complexity Analysis
On the basis of comparison with the middle value, we are reducing the input size by 1/2 at every step of recursion. In the worst case, Recursion will terminate at the base case which is l > r i.e the case of unsuccessful search. (Think!)
Suppose, T(n) = Time complexity of searching the value K in n size array. To summerise,
- Divide: It is O(1) operation because the middle index can be calculated in constant time.
- Conquer: It is the time complexity of recursively solving the one sub-problem of size n/2 i.e. T(n/2).
- Combine: It is O(1) operation.
The recurrence relation for the above is: T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1)
Time complexity is O(log n), which is much faster than O(n) algorithm of linear search. Note: We can solve the above recurrence relation by recursion tree method or master theorem. (How? Think!)
Critical Ideas to think
- Can we use some hypothesis to analyze the time complexity of binary search?
- Think about the recursive and iterative implementation of the binary search algorithms. Also, compare the space complexity of both?
- Prepare a list of the problems where we can apply the ideas similar to the binary search for the solution.
- Explore the idea of Ternary Search where we apply the divide and conquer approach but we divide the given array into three parts. Why is Binary Search preferred over Ternary Search?
Example 2: Merge Sort
Merge Sort is an efficient O(nlog n) sorting algorithm and It uses the divide-and-conquer approach. The algorithm works as follows:
- Divide: Divide the n elements sequence into two equal size subsequences of n/2 element each
- Conquer: Sort the two sub-sequences recursively using merge sort.
- Combine: Merge the two sorted subsequences to produce a single sorted sequence.
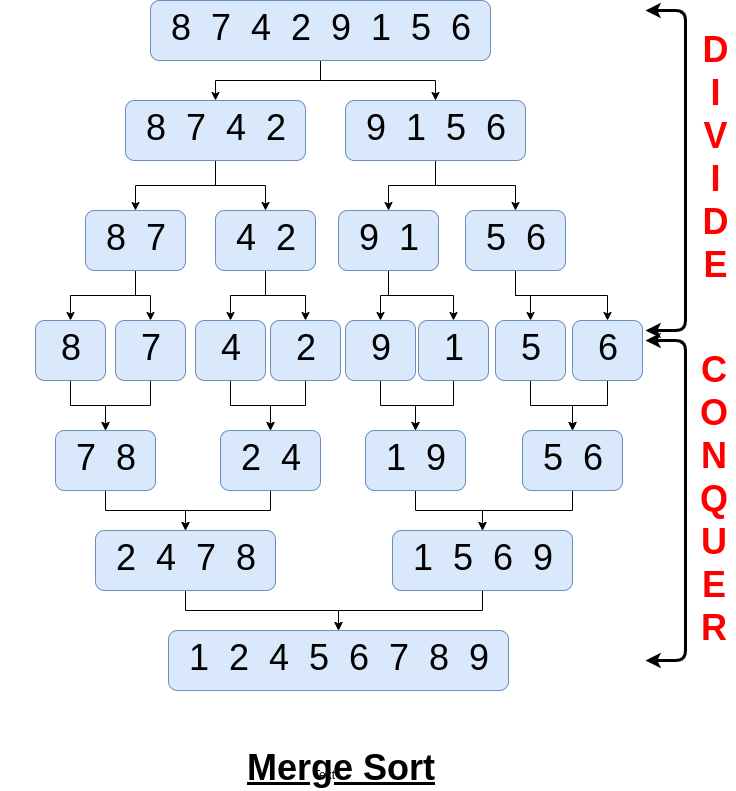
Solution Steps
Recursive Call: mergeSort(A[], l, r)
- Divide: Calculate the middle index of the array.
- Conquer: Recursively solve the two smaller sub-problems
1) Sort the first half: mergeSort(A, l, mid)
2) Sort the second half: mergeSort(A, mid+1, r)
- Combine: Merge the two sorted halves by merge function
merge(A, l, mid, r)
- Base Case: if (l == r) then return -1. This is the case of a single element (Think!)
Complexity Analysis
Suppose, T(n) = Time complexity of searching the value K in N size array. To summerise,
- Divide: It is O(1) operation because mid can be calculated in constant time.
- Conquer: Time complexity of recursively solving the two sub-problem of size n/2 i.e. 2 T(n/2)
- Combine: The time complexity of this part is O(n) because merging two sorted array or lists requires O(n) operation (Think!)
The recurrence relation for the above is: T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n)
So, the time complexity of the merge sort is O(nlog n). Note: We can solve the above recurrence relation by recursion tree method or master theorem.
Critical Ideas to think!
- How we implement the merge sort algorithm? Can we think of an Iterative version of it?
- How can we design the algorithm for merging two sorted half? Hint: This is an important two pointer approach.
- Think about the base case of the merge sort.
- Can we solve other problems using a similar approach?
- Explore the divide and conquer algorithm of quick-sort.
Problem solving concepts and tips
- Usually, we solve a divide and conquer problems using only 2 subproblems. But there are few cases where we use more than two subproblems for the solution. (Think and explore!)
- Several problems can be solved using the idea similar to the merge sort and binary search.
- This is a very good algorithm design strategy to learn about recursive problem solving. Before understanding dynamic programming and backtracking, We always suggest to understand this approach.
- The correct base case is very important for correctness!
- Subproblems are always independent in divide conquer algorithms because every subproblem is working on the different parts of the given input (Think!)
- Iterative Implementation: Divide-and-conquer algorithms can also be implemented by a non-recursive algorithm. In this case, we need to store the solution of smaller subproblems in a explicit stack data structure.
- In recursive algorithms, the call stack is used which also takes the memory which leads to an increase in space complexity of the algorithm.
Critical concepts to explore further
- Divide and Conquer Vs Dynamic Programming
- Iterative implementation of recursive algorithms
- Analysis of recursion by recursion tree method
- Analysis of recursion by master theorem method
Important Problems/Real-Life Applications
- Binary search
- Merge sort
- Quick sort
- Karatsuba algorithm for fast multiplication
- Finding convex hull
- Strassen’s matrix multiplication
- Find the closest pair of points
- Algorithm for fast Fourier transform
Suggested Problems to solve
- Median of two sorted arrays of the same size
- Inversion count in an array
- Search for a Range in a sorted array
- Median in a row-wise sorted matrix
- Longest Common Prefix
- Find the minimum element in sorted and rotated array
- Find an element in Bitonic array
Happy coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course — Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Divide & Conquer vs Dynamic Programming
Divide and Conquer and Dynamic Programming are two most used problem-solving skills in Data Structures. In this blog, we will see the similarities and difference between Dynamic Programming and Divide-and-Conquer approaches.
AfterAcademy Tech
Idea of Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming is one of the most commonly used approach of problem-solving during coding interviews. We will discuss how can we approach to a problem using Dynamic Programming and also discuss the concept of Time-Memory Trade-Off.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is iteration in programming?
The repeated execution of some groups of code statements in a program is called iteration. We will discuss the idea of iteration in detail in this blog.
AfterAcademy Tech
Getting started with Competitive Programming
In this blog, we will see how to get started with Competitive Programming. Competitive Programming is very important because in every interview you will be asked to write some code. So, let's learn together.
