What are ICMP and IGMP protocols?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
29 Feb 2020
When you are not connected to the internet and search for any website then you get an error message like destination unreachable or time limit exceeded etc. These messages are displayed through the ICMP protocol. The IP protocol does not have any mechanism for error reporting and sending query messages. This problem is resolved by the ICMP protocol.
Online streaming of videos and games generally uses the IGMP protocol for more efficient use of the resources. In this blog, we will learn about these two protocols of the TCP/IP. So, let's get started.
ICMP
ICMP or Internet Control Message Protocol is one of the major protocols of the TCP/IP. ICMP is a mechanism used by the host, routers, and gateways to send error messages back to the sender. As the IP does not provide any mechanism for error reporting and control, ICMP has been designed to compensate for these deficiencies of the IP. However, it only reports the error and doesn't correct the error.
The ICMP messages are divided into two categories:
- Error Message
- Query Message
Error Message
The error messages report the problems which may be faced by the hosts or routers when they process the IP packet.
- Destination Unreachable: When any router or gateway determines that the packet cannot be sent(due to link failure, congestion, etc) to the final destination then it sends an ICMP destination unreachable message to the source. Not only the routers but the destination host can also send the ICMP error message if there is any failure at the destination like hardware failure, port failure, etc.
- Source Quench: A source quench is a request by the receiver to the sending host or sender to reduce the rate at which the sender is sending the data. This message is sent by the receiver when it has congestion and there are chances that the packet may get lost if the sender keeps on sending the packets at the same rate.
- Parameter Problem: When the packet is received by the router then the calculated checksum should be equal to the received checksum. If there is any ambiguity then the packet is dropped by the router and the parameter problem message is sent.
- Time Exceeded: Whenever the TTL(Time to Live) field of the datagram reduces to zero then the router discards the datagram and sends the time exceeded message to the source.
- Route Redirect: If any router determines that the host has incorrectly sent the packet to the different router the router uses the route redirect message to inform the host to update its routing information. So, it helps in improving the efficiency of the routing process.
Query Message
The ICMP protocol can diagnose some network problems also. Query messages help the hosts to get some specific information from a router or another host.
- TimeStamp Request/Reply: Host and routers determine the round trip- time required for an IP datagram to travel between hosts or routers. It can also be used to synchronize the clocks in two systems.
- Router Solicitation and Advertisement: If the host wants to send the data to a host on another network then it needs to know the address of the routers connected. The host also needs to know if routers are alive and operational. All these functions are provided by the router solicitation and advertisement message.
- Address Mask Request/Reply: The host broadcast the address mask request if it does not know the address of the router. The router receiving the address mask request replies with the necessary mask for the host.
- Echo Request/ Echo Reply: It a command designed checking the connectivity between two hosts. Example: ping command.
Let's say you want to check the connectivity between your computer and the Google server. You can do this by writing the command “ping www.google.com” in the command line.
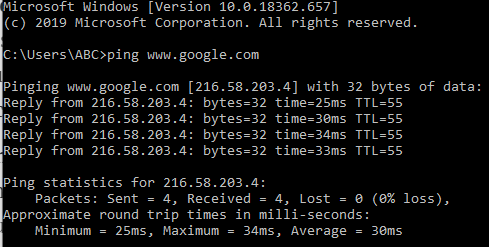
When the ping command is invoked then the ICMP echo request message is sent to the target host(google, here). If the target is connected to the network and operational then it sends an echo reply message as an acknowledgement.
IGMP
IGMP is also a protocol of the TCP/IP. Internet Group Message Protocol is an Internet protocol that manages multicast group membership on IP networks. Multicast routers are used to send the packets to all the hosts that are having the membership of a particular group. These routers receive many packets that are to be transmitted to various groups and they just can't broadcast it as it will increase the load on the network.
So to overcome this problem a list of groups and their members is maintained and IGMP helps the multicast router in doing so. The multicast router has a list of the multicast address for which there are any members in the network. There is a multicast router for each group that distributes the multicast traffic of the group to the members of that group.
Major goals of the IGMP protocol.
- To inform the local multicast router that the host wants to receive the multicast traffic of a particular group.
- To inform the local multicast router that the host wants to leave a particular group.
Versions of IGMP
- IGMPv1: It was the first version where the host announced that it wants to receive the traffic of a particular multicast group. 0.0.0.0 is defined as the group address and the 224.0.0.1 as the destination address for the general IGMP requests. The default interval for these requests which is sent automatically by the routers is 60 seconds. There was no system of leaving a multicast group. Only a timeout(delay timer 180 seconds)removes the respective host from groups they’re in. Suppose the host which is in a particular group closes its system. This results in a situation where the traffic is sent to the host even if is not accepting the traffic. When the router discovers after some time that the host is no longer accepting the traffic then the multicast traffic is stopped. This problem was resolved in the next version.
- IGMPv2: The group address (0.0.0.0) and destination address(224.0.0.1) remain unchanged. but, the default interval for these requests which is sent automatically by the routers is increased to 125 seconds. The most important feature added in this version is “leave message” which a host can send if it wants to leave a group. This allows the router to stop an unnecessary multicast of traffic.
- IGMPv3: The group address (0.0.0.0) and destination address(224.0.0.1) remain unchanged and the default interval for these requests which is sent automatically by the routers is 125 seconds. The most feature added in this version was the option to select the source of the multicast stream. This reduces the demands on the network and ensures greater security during transmission.
This is was a brief overview of ICMP and IGMP protocols. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are Protocols and what are the key elements of protocols?
In this blog, we will learn about Protocols. We will also learn about the types, key elements, and functionalities of protocols used in computer network and data communication.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is Stop and Wait protocol?
In this blog, we will learn one of the flow control method i.e Stop and Wait Protocol. We will discuss various situations that can occur while transmitting the data. We will also mathematically derive the efficiency and the throughput of this protocol.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is RIP(Routing Information Protocol)?
In this blog, we will learn about what is RIP and how does it work. We will also discuss what are versions of RIP and various RIP timers. In last will see the advantages and disadvantages of this protocol.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is ARP and how does it work?
In this blog, we will learn what is Address Resolution Protocol and how it helps in communication between two devices. We will also discuss what are the problems that can arise while using this protocol and see sample examples of ARP packets which are captured.
