Validate Stack Sequences
AfterAcademy Tech
•
05 Oct 2020
Difficulty: Medium
Understanding The Problem
Problem Statement
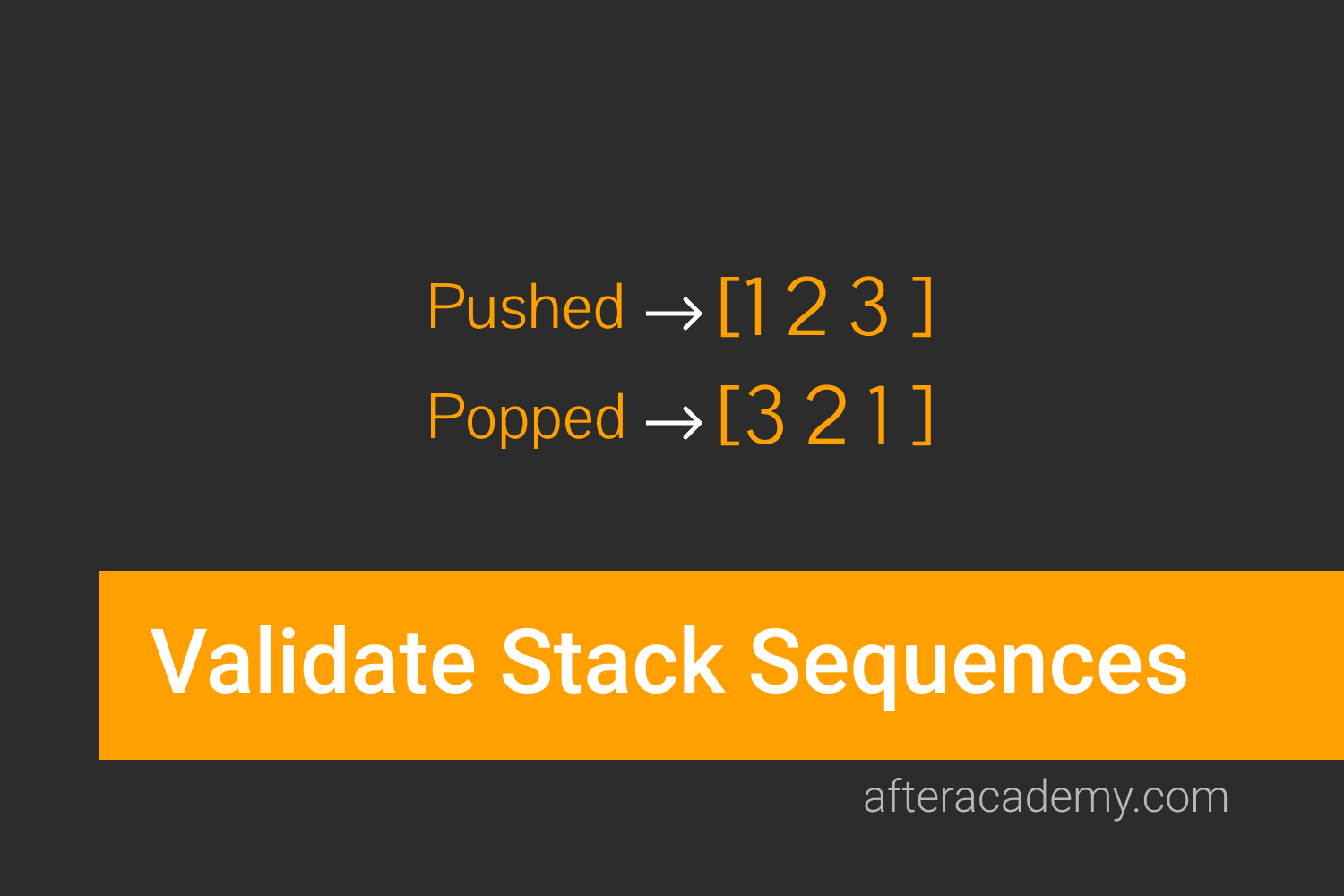
Given two sequences pushed and popped with distinct values, write a program to return true if and only if this could have been the result of a sequence of push and pop operations on an initially empty stack.
Problem Note
- pushed is a permutation of popped.
- pushed and popped have distinct values.
Example 1
Input: pushed = [5, 10, 15, 20, 25], popped = [20, 25, 15, 10, 5]
Output: 1
Explanation: We might do the following sequence:
push(5), push(10), push(15), push(20), pop() -> 20,
push(25), pop()-> 25, pop()-> 15, pop()-> 10, pop()-> 5
Example 2
Input: pushed = [5, 10, 15, 20, 25], popped = [20, 15, 25, 5, 10]
Output: 0
Explanation: 5 cannot be popped before 10.
Solution
To validate the pushed and popped operation on an empty stack, we can follow a Greedy approach. A stack performs two operations push to the top of the stack and pop from the top of the stack.
The sequence will be valid if we can perform push and pop operation such that all the values stored in the pushed and popped array will be exhausted without interfering with the sequence.
How can we use a stack to solve this problem?
The simpler way to proceed is to use an empty stack and start pushing the elements of the pushed array sequentially in the stack and comparing every top element of the stack with the front element of the popped array.
If the top element of the stack is at the front of the popped array then we can pop the element from the stack and increment the popped array pointer by one, otherwise, we can push the front element of the pushed array in the stack and increment the popped array pointer by one. If in this process, all the elements of the popped array gets exhausted, then our sequence is valid.
Try this problem here.
Solution Step
- Create an empty stack and push the first element of
pushedarray - Place two pointers on the
pushedandpoppedarray. - Compare the top element of the stack with the front element of
poppedarray
- If both of them are the same, then we have to pop the top element of the stack and increment the
poppedarray pointer by one - If both of them are not the same, then we have to push the front element of
pushedarray into the stack and increment thepushedarray pointer by one
4. Repeat step 2 to 3, until the stack becomes empty.
Pseudo Code
bool validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack stack
int j = 0
for (int i = 0 to i < pushed.size()) {
stack.push(pushed[i])
while (stack is not empty and stack.top() is popped[j]) {
stack.pop()
j = j + 1
}
}
if(stack is empty)
return true
else
return false
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)(How?)
Critical Ideas To Think
- We have used while loop inside a for loop, then how come the time complexity is O(n)? Answer: If we follow the logic of pseudocode, we are visiting each element of
pushedandpoppedarray only once. - What will be the case when the stack will not be empty at the end? Answer: When we have an invalid sequence, the stack will not be empty at the end. Try the above example 2 on this pseudocode.
- How this is a greedy approach? Read here to learn about greedy algorithms.
- What does the variable
jrepresent in the pseudocode? - Can we solve this problem by using a queue, instead of a stack?
- Will this approach work if the
pushedarray contains repeated elements?
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Activity selection problem
- Huffman coding
- Water connection problem
- Graph coloring
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Sort A Stack Using Another Stack
Given a stack, you have to sort it in ascending order. You can use another stack if you need auxiliary space. The problem is asked in Google, Microsoft and Amazon and requires knowledge of Stack and recursion to solve it.

AfterAcademy Tech
Stack and its basic Operations
Stack is a very useful concept that a good programmer could use for their benefit. We will be discussing the basic design of stack and the operations that can be performed on it. We shall be also discussing the implementation of stack.

AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Stack Using Recursion
Given a stack of integers st, write a program to reverse the stack using recursion. This problem will clear the concept of recursion.
AfterAcademy Tech
Min Stack Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Yahoo and Adobe. The problem is to design a stack that will support push(), pop(), top() and getMin() operation in constant time. We will be discussing two different ways to approach this problem.
